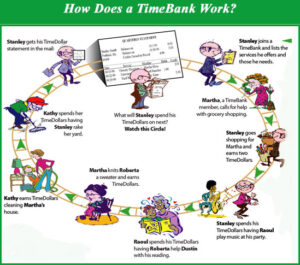
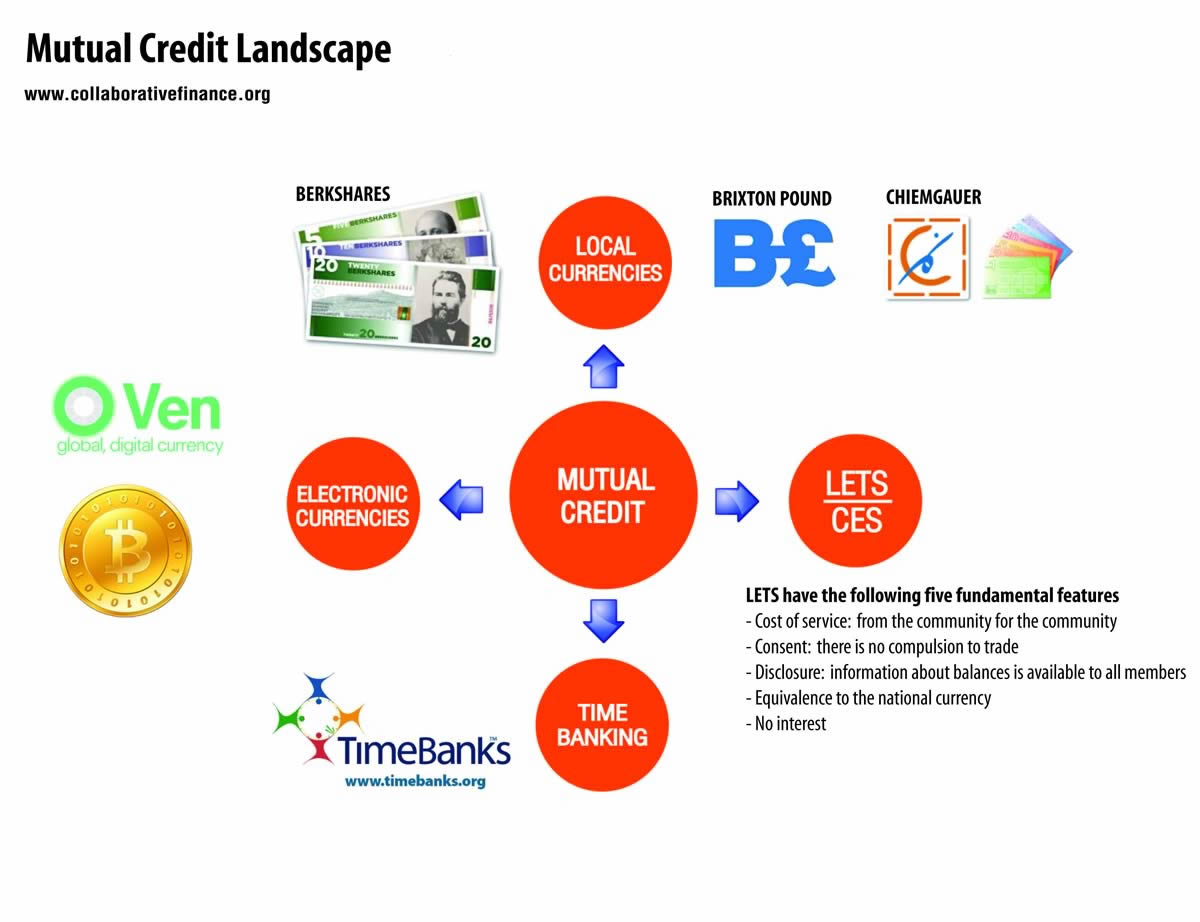
 Mutual credit is a type of alternative currency in which the currency used in a transaction can be created at the time of the transaction. LETS are mutual credit systems. Typically this involves keeping track of each individual’s credit or debit balance. Although the effect is like a loan, no interest is charged, and since mutual credit allows for trading and cancelling balances with others, debts can be paid off indirectly.
Mutual credit is a type of alternative currency in which the currency used in a transaction can be created at the time of the transaction. LETS are mutual credit systems. Typically this involves keeping track of each individual’s credit or debit balance. Although the effect is like a loan, no interest is charged, and since mutual credit allows for trading and cancelling balances with others, debts can be paid off indirectly.
One economic advantage of mutual credit is that the currency supply is self-regulating—the money supply expands and contracts as needed, without any managing authority. The availability of interest-free loans is a great advantage to members of the system.
One downside of mutual credit, as with any form of credit, is the possibility of exploiting the system by running up a negative balance and then leaving. This problem is often addressed by caps on negative balance which can be raised as balances are paid off, or by limiting the system to a small, close-knit community based on trust, where the community holds people accountable. For this reason, most mutual credit systems are small (under 2000 members).
LETS, the Community Exchange System and the Cincinnati Time Store are examples of mutual credit systems. A number of different mutual credit systems have been proposed. Mutual credit can be combined with a number of features of alternative currency systems. For example, it is usually (but does not need to be) a local currency, and it can have a demurrage fee for the holding of balances.